Why is Creating a Virtual Classroom Important?
Stay Ahead with Insights from Precipoint!
Welcome to our newsletter! Be the first to know about our latest products, services, webinars, and happenings in PreciPoint. Don't miss out on this opportunity to stay informed. Subscribe to our newsletter today!
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to our privacy policy.
Step 1: Glass Slides
Step 2: Digital Microscope/ Slide Scanner
- Do I have to continuously scan new slides or is a one-time scanning of a sample-set sufficient?
- How many slides do I need to be scanned per day?
- What type of specimen is being scanned, and what type of objective do I need?
- Do I need pre-scanned slides to distribute and share?
- Or can I present the slides live with real-time scanning via screen sharing?
To digitize your samples, you can choose between various systems:
1. Microscopes with cameras attached to the top
They only allow for a live presentation of the shown region of interest and are limited in their field of view. You can then share the image from the camera via screen sharing. They are usually more affordable, but also limited.
2. Microscope and scanner hybrids
They do both whole slide scanning and live viewing of the samples. Live viewing means, you can instantly navigate through the whole inserted slide and look at every detail, without having to wait. This enables you to instantly present slides directly on the microscope to the audience. But it will not create a file. Whole slide scanning is used to create a virtual microscopy file of the slide. In that way, you can independently work online on complete virtual slides and share them. These hybrid systems offer the greatest flexibility.
3. Dedicated scanners
Types of Digital Microscopes and Scanners
Scanning Capabilities
Many qualifications depend on the department or application that is being addressed. There are scanners out in the market that can scan at 100x oil immersion which might be better for educating students who are looking at blood cell morphology and then there are some that are limited on their scanning capabilities. But once a scanner or digital microscope/hybrid has been selected then the process of digitizing the glass slides can commence.
Available Technologies
Conventional manual digital microscopes (microscopes with cameras attached to the top), hybrid systems, and slide scanners are currently offered by several companies globally. The prices can vary from a few thousand to anywhere upwards of several hundred thousand euros, for example, Motic, Hamamatsu, Zeiss, 3DHistech, Leica, Aperio, Philips, and PreciPoint all offer scanners and/or digital microscopes with different capabilities.
Throughput Options
There are differences depending on the throughput demand. Some come with a slide loader, which makes it possible to load several slides into a cassette. In the next step, the slide scanner can process them one after another. However, digital microscopes or hybrid systems that must be manually fed slides are much more affordable and usually work well for education purposes.
Step 3: Image Storage (Slide Scanners)
How much space is needed for virtual slides?
Once the glass slide has gone through the scanning process, a place to store the digital file must be implemented. For a whole slide image (WSI), the file size can range on average from several MB up to 70GB, and this depends on the magnification, the physical size of the sample, and most important the file format at which the slide is scanned [2]. Some file formats are relatively small due to effective compression. Another factor is the size of the ROI (region of interest) that is scanned.
For example, if a professor is teaching a class about hematology and scanned the slides at 100x oil immersion, then those scans are going to yield a large amount of data. If you compare that to someone who is teaching a class about pathology and they are only using a 20x objective to scan, the pathology slides would be much smaller in size. So, it is crucial to look at the capacity needed for storage.
Where can the virtual slides be stored?
When it comes to storing images on a database there are only two ways. You can have the database be located on-premises (locally) or in the cloud (web-based). Most hospitals and universities require the database to be on-premises, this is due to privacy data security, and because existing laboratory information systems may require a locally running server. There are benefits for both on-premises and cloud-based storage, but as stated above, on-premises has the highest demand. Contrary to a popular belief a database that is cloud-based usually has better scalability and data security. For students, it is much easier to access a cloud-based storage server because they do not have to connect to a VPN to access the data that is stored locally.
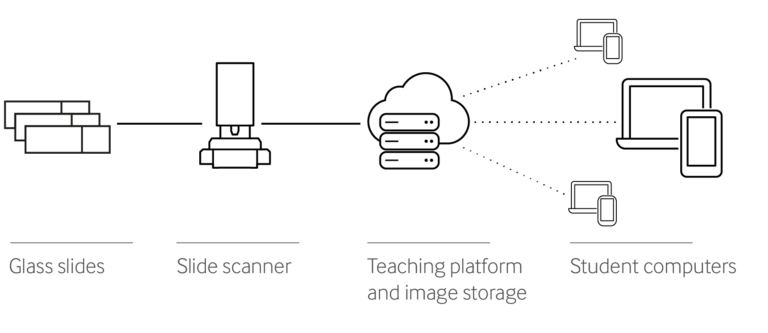
Step 4: Video Conferencing Software and Teaching Platform
The basic equipment you will need consists of:
1. Video conferencing software
2. Webcam (integrated into your notebook or detachable)
3. Microphone (notebook, headset, or stand-alone-microphone)
4. Audio (notebook or headphones)
5. Filesharing for lesson materials (GoogleDrive, OneDrive, teaching-platforms)
6. Digital microscopy slides (live or pre-scanned)
Teaching platform
Some commercial teaching platforms go beyond just storing and viewing slides. Some allow academic tutors to build extensive libraries of slides for review by students using the web. Virtual slides, pre-annotated cases, exams, course notes, and multimedia content can all be integrated into a teaching platform, creating a flexible digital slide resource accessible from anywhere with internet access.
Most teaching platforms have well designed graphical user interfaces and provide many teacher-friendly features like visibility control that allows the administrator to sequentially release content to users. Administrators can also define customer access to virtual slides for individual students and specific student groups. Teaching platforms can be used to completely change the dynamic in the classroom and even help students work outside of class and continue their education at their own speed [3].
Step 5: Viewing/ Observation













