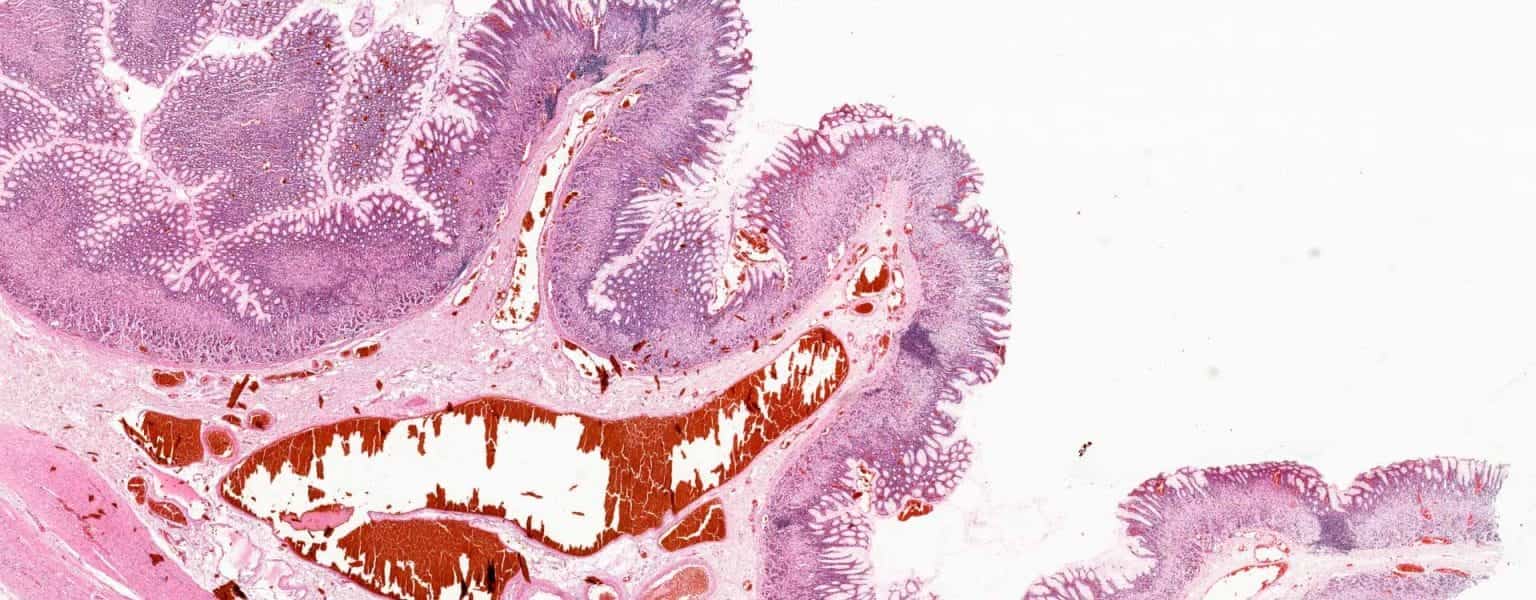
Synopsis
Brightfield microscopy is one of the oldest and most widely used techniques among researchers and medical experts. The image in a brightfield microscope is formed with the help of the light that goes through the specimen and forms the light image against the dark background. The microscope has helped in the discovery of cells, microorganisms, viruses, and cancer, and it has also been used in the development of genetics. Some of its advantages are its simplicity and versatility, viewing detailed images, its non-destructive technique, and compatibility with other techniques. This article will tell you more about the microscope and its advantages and limitations.
One of the oldest and most used techniques in microscopy is brightfield microscopy. It allows for the observation of living cells, tissues, and other biological specimens for educational and research purposes. The name “brightfield” refers to the fact that the image is formed with “the help” of the light that goes through the specimen and forms the light image against the dark background. This technique has also been used to explore many topics in biology and medicine. The basic principle that brightfield technology uses is simple; the equipment is not expensive; and it allows for an observation that won’t harm the quality of the specimen. In general, brightfield microscopy can be used in the cell, tissue, and other biological specimen research, but it can also be very helpful in the observation and research of non-biological materials such as diverse types of minerals and metals.
Stay Ahead with Insights from Precipoint!
Welcome to our newsletter! Be the first to know about our latest products, services, webinars, and happenings in PreciPoint. Don't miss out on this opportunity to stay informed. Subscribe to our newsletter today!
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to our privacy policy.
Who Invented the Brightfield Microscope?
The brightfield microscope was invented over time through the contributions of multiple scientists. The basic principles of the brightfield microscope were established by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century when he created simple microscopes for observing tiny organisms. However, the design and development of more advanced brightfield microscopes involved the work of various scientists in the 19th and 20th centuries.
How Does Brightfield Microscopy Work?
Brightfield microscopy is the most basic of all the optical microscopy illumination methods. It uses the transmitted white light method which illuminates from below and is observed from above. The technique relies on the sample’s contrast, created by the authentication of transmitted light in denser regions. This method is a common choice in the array of illumination methods for light microscopes. The resulting image typically portrays a dark sample against a bright background. In the dynamic world of sample observation, this technique’s simplicity contributes to its widespread utilization and popularity.
Easy and Simple Technique
The researcher or medical expert usually needs a light source, a condenser lens, an objective lens, and an eyepiece lens. Typically, a halogen lamp serves as a light source. The light is directed through the condenser lens, which focuses the light on the specimen. The objective lens is located under the specimen. They magnify the image and project it upward through the eyepiece lens. They further magnify the image for the observer.

What Are the Various Applications of Brightfield Microscopy?
Bright-field microscopy finds diverse applications across scientific disciplines, making it a versatile tool in research, education, and various industries. In biological research, it is pivotal for examining stained specimens like tissues, cells, and microorganisms, as well as observing live cells in culture. In medical diagnostics, bright-field microscopy plays a crucial role in clinical pathology, analyzing blood smears, urine samples, and biopsy specimens. It also aids in identifying pathogens in clinical microbiology. In material science, this technique is employed for quality control and studying the microstructure of materials such as metals and polymers. Bright-field microscopy is extensively used in education, serving as a foundational tool for introductory microscopy in biology and related fields. Industries, including food and beverage, utilize it for quality control and contamination analysis. Additionally, it is applied in environmental science, forensic science, pharmaceutical research, botany, and entomology, showcasing its broad impact in advancing knowledge and applications across various scientific domains. Brightfield microscopy was instrumental in important discoveries. Some of the discoveries include:
- Discovery of Cells: Thanks to the invention of the microscope by Anton van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century, it became possible to observe and research cells. That led to the development of brightfield microscopy and cell theory in the 17th century, one of the fundamental theories in biology.
- Discovery of Microorganisms: Bacteria and protozoa were some of the microorganisms observed and studied by using brightfield microscopy. These microorganisms were previously invisible to the naked eye. This led to a new knowledge base about the role of microorganisms in diseases and the development of biology in general.
- Discovery of Viruses: Viruses, even smaller than bacteria, were thought to be non-living. Using brightfield microscopy it was possible to study and observe these microorganisms and better understand viruses in diseases.
- Organelles: The technique of brightfield microscopy was also used to study the internal structure of cells, known as organelles. Using brightfield microscopy, researchers became familiar with mitochondria, the nucleus, and the endoplasmic reticulum. Brightfield microscopy helped researchers understand the role of organelles in cell functioning.
- Development of Genetics: Brightfield microscopy greatly influenced the development of genetics. It allowed researchers and medical experts to observe chromosomes, the genetic material of cells. The development of genetics led to a better understanding of the role of genes in the studies of inheritance and traits.
- Discovery of Cancer: Brightfield microscopy made it easier to better understand the causes and structure of cancer disease. It also helped to develop the treatments like chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
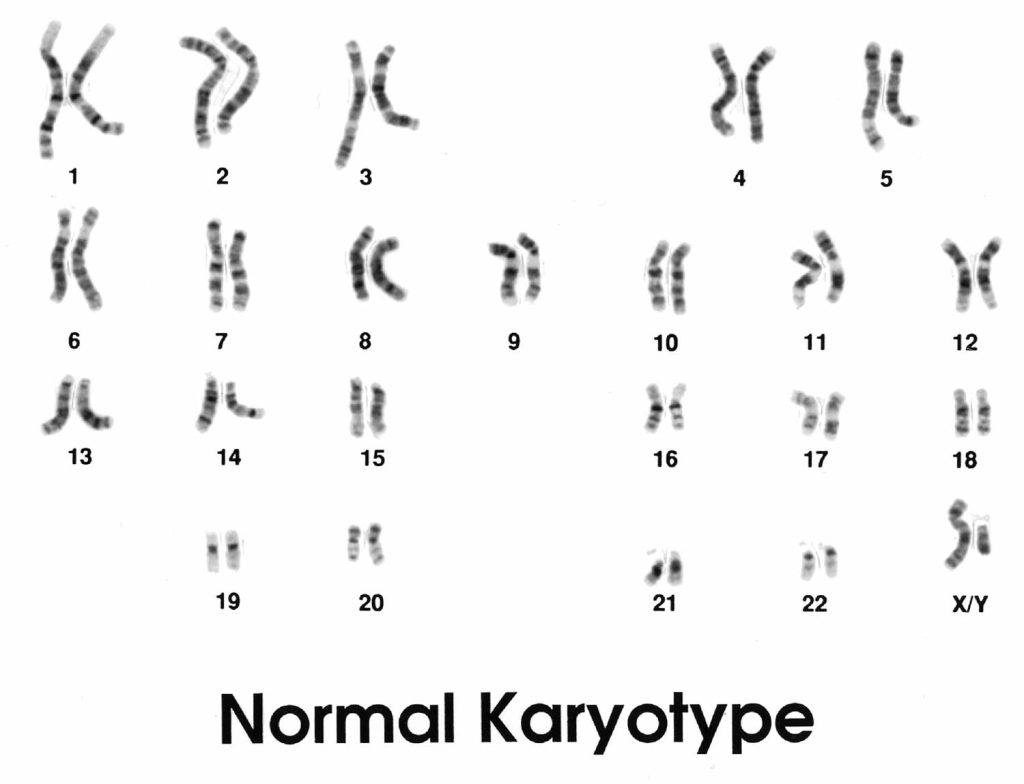
When we see all these discoveries, it’s easy to conclude that brightfield microscopy is a fundamental tool in biology and medicine that helps in better understanding of the organisms at the cellular and molecular levels.
Brightfield Microscopy: Advantages
Brightfield microscopy is known for its simplicity. No special dyes or stains are needed, and no special equipment is needed. As a result, the technique is inexpensive and easily accessible, making it ideal for use in educational and research settings.
Other Advantages Include
- Detailed Images: High-resolution images, ideal for detailed observation.
- Versatility: Brightfield microscopy can not only be used with diverse biological materials like tissues, cells, and other specimens but also with non-biological materials like minerals and metals.
- Non-destructive Specimen: It uses a non-destructive technique, which means the specimen is not damaged or altered during the imaging process. Additionally, the specimen can be studied multiple times.
- Availability: Brightfield microscopy techniques require simple and inexpensive equipment. It is easily accessible by researchers and educators.
- Compatibility with Other Techniques: The technique used in brightfield microscopy can be easily combined with others like fluorescence or electron microscopy if the researcher or medical expert needs to obtain a higher quality of images or get more data from the specimen.

What Are the Limitations of Brightfield Microscope?
However, there are a few drawbacks as well. One of the main disadvantages of brightfield microscopy is that it cannot detect structures or molecules that don’t absorb or scatter light. It can also be difficult to distinguish between different structures that are located at different depths within the specimen. This can be quite problematic when working with transparent or semi-transparent samples. To overcome the disadvantages, several variations of brightfield microscopy have been developed. One of the most widely used is phase contrast microscopy, first used in the early 1930s. The contrast microscope uses a special lens to increase the contrast between transparent and semi-transparent specimens. There is a phase shift in the light passing through the specimen.
Darkfield microscopy has been used since the early 20th century. It is another variation of brightfield microscopy that has gained popularity in recent years. The light source does not directly illuminate the specimen but instead reflects into the objective lens. An image obtained as a result appears dark, with bright spots at the place where the light is reflected off the specimen. It is especially useful when a researcher needs to observe smaller, transparent samples, or microorganisms.
Brightfield microscopy is a very useful technique and very helpful for researchers and medical experts who need to observe cells, tissues, and other biological specimens. This technique is simple, inexpensive, and easily accessible, but it has its limitations. To overcome these limitations diverse variants like fluorescence or darkfield illumination were developed. Phase contrast microscopy uses a special lens to increase the contrast between transparent and semi-transparent specimens. Darkfield microscopy is especially useful for observing smaller or transparent samples. Both variants proved quite helpful in obtaining the maximum possible efficiency and work quality. Digital microscopes from PreciPoint also offer several benefits. O8 oil digital microscope and slide scanner serve as both a digital microscope and a scanner, offering completely new possibilities for your workflow.